Marketing Channels Can Achieve Economies of Scale Through
ix MIN READ
Achieving Economies of Scale
Understanding Why Bigger Tin Be Better

© GettyImages
ake1150sb
Load upward on the benefits from economies of calibration
"Biggest is best" and "Stack 'em high, sell 'em cheap" are non the most elegant phrases in the English linguistic communication. But they accurately describe an important business reality.
This is the idea that, as a company grows and information technology needs to brand more of a product, the average toll of making each item falls, resulting in a rise in profits. Similarly, if a store buys a production in bulk, it can often negotiate a discount from the wholesaler and, equally a result, sell the item at a cheaper price than its rivals. Economists call this "economies of scale."
In this article, we'll await at the two dissimilar types of economies of scale that can give businesses a competitive advantage. We'll also explore what happens when organizations get likewise big, and are hitting past "diseconomies of scale."
Economies of Scale Definition
Economies of scale are cost savings that a visitor (and, by default, its customers) can reap as a result of efficient production processes. More often than not, these cost savings are achieved considering the average of cost of producing something falls as the volume being produced increases.
In brusk, yous get more than for your money when your organization achieves economies of scale. And so, while yous may incur initial extra costs by investing in new machinery, additional labor or more raw materials, yous salvage money on the average cost of each unit you produce (see effigy ane, beneath).
Effigy 1. Economies of Scale by Cost and Quantity Produced
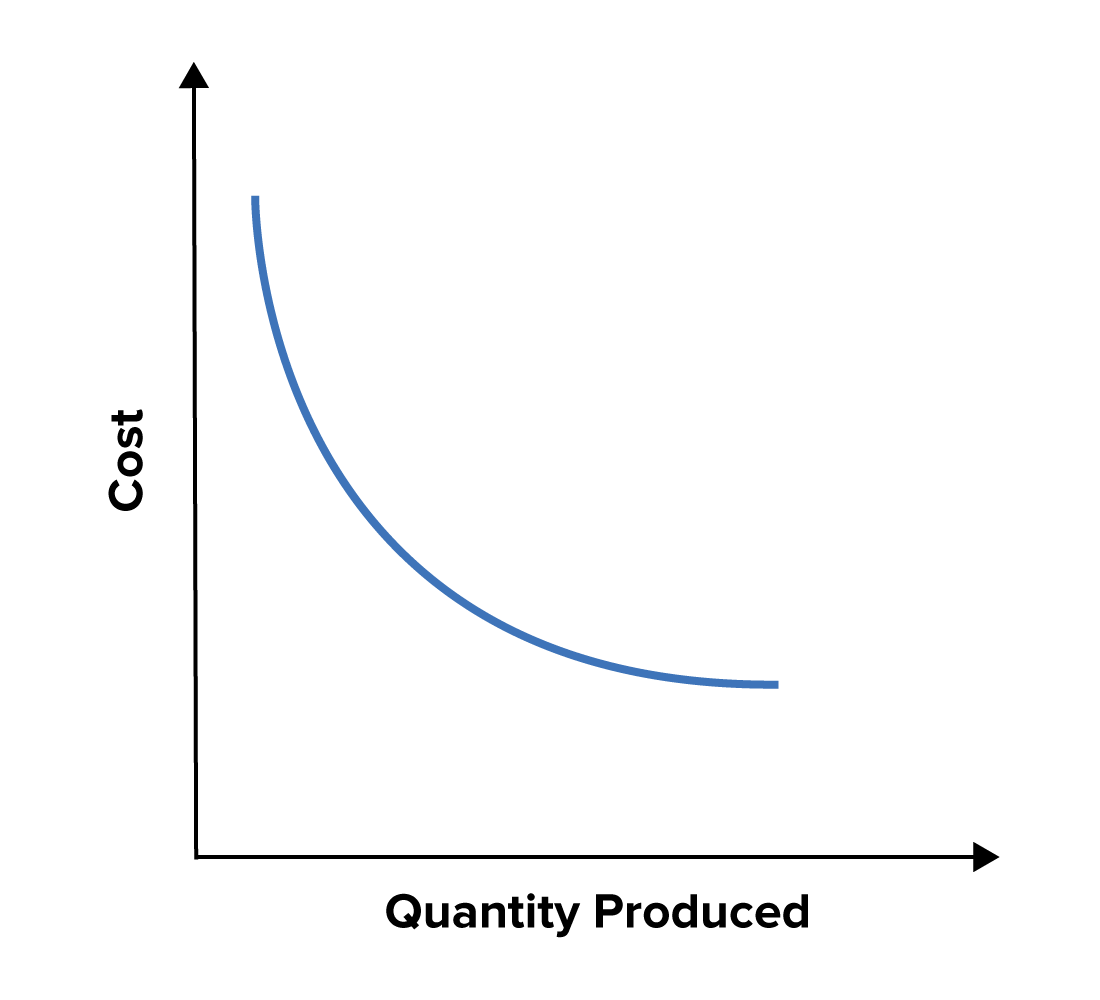
This basic principle has been the driving force behind many major economic developments, such as the industrial revolution and mass production. And it is why bigger companies are often more efficient and can deliver appurtenances and services at a low price, yet nonetheless brand a good for you turn a profit.
Recall of how Ford's assembly line inverse the face up of machine manufacturing, for instance. And consider how Walmart's "everything under one roof" style and immense purchasing ability allows it to beat its competitors on price.
Economies of Scale Instance
Now let's look at an case of how economies of scale can work in business:
The cost of making 200 copies of your system's new product brochure is $four,000. The average unit cost is $20 (that'southward $4,000 divided by 200).
But to make 1,000 copies is only $5,000, an average cost of $5 a copy.
This is because the chief element of the cost of making the brochure is labor for designing and editing the cloth, and setting up the printing press. These are fixed costs that remain the same no matter how many brochures y'all produce. Y'all will therefore save coin by producing more product brochures.
Internal Economies of Scale
In general, there are two different types of economies of scale – internal and external. Let'south accept a look at how internal economies of scale work first.
Internal economies of scale are cost-saving factors that are specific to organizations, regardless of the industry or environment that they operate in. There are 5 types of internal economies of scale that tin do good companies:
1. Technical
You tin achieve technical economies of scale by improving the efficiency and the size of your production process. For example:
- Dividing your product procedure into separate tasks can increase productivity. Your workers will likely become more specialized and efficient, and you can slash unit costs past using mass production techniques, such as investing in specialist machinery.
- Edifice on your experience tin improve the efficiency of your processes because you have accrued greater noesis and enquiry in a specific surface area. This can frequently lower product costs.
- Taking advantage of the law of increased dimensions, or "cubic police" promotes economies of calibration in industries such every bit ship and logistics. If y'all double a container'due south length and height, for example, its capacity increases 400 percent. Think of supertankers or Amazon'due south huge warehouses.
2. Purchasing
Majority buying tin can cut costs dramatically, as nosotros can see from the brochure example, to a higher place. If you lot're a large manufacturer, y'all'll likely have more bargaining power than your smaller competitors to negotiate lower prices with your suppliers.
Bigger firms can also get improve delivery rates, considering they crave more products to exist moved. Efficient inventory or stock management is another style to reduce average unit costs, by non paying for, or unnecessarily holding on to, component parts in-store.
3. Managerial
You can reach managerial economies of calibration by investing in expertise as your system grows. Specialist managers who oversee and improve production systems tin streamline processes and increment productivity, resulting in lower boilerplate unit of measurement costs and economies of calibration.
4. Financial
Larger organizations oft have better credit ratings than smaller ones, because they have more assets to use as collateral. This means that they tin can borrow more than cheaply in order to finance investment and realize even greater economies of scale. They then reap further rewards from their investment considering the lower involvement rates they are offered mean that it costs them less to borrow.
Companies that are quoted on the stock marketplace have further access to new finance, and thus to fifty-fifty greater economies of scale through the sale of equities or shares.
five. Take chances-Bearing
The more a company diversifies its activities and spreads its costs, the less overall risk information technology assumes in any one line of business concern and the lower its unit costs will be.
The ability to take the risk of carrying out complicated and expensive research is some other benefit for large firms. Big pharmaceuticals companies, for case, are able to profit from this aspect of economies of calibration. Bigger companies can also afford to market place and advertise their products more effectively.
External Economies of Scale
External economies of scale occur where a company gains advantages every bit a outcome of events and developments in their industry and the wider external environment.
Here are some examples:
- Industry growth may let you admission to specialist or lower-price suppliers.
- Low need and large supply may bring downwards the cost of your supplies.
- Where many similar companies operate in the same expanse as you, there may be a bigger pool of pre-trained people to recruit from.
- Industry infrastructure may already exist in place to support your organization'due south growth.
- Training facilities may be more readily available.
- A skilful transportation network may be available.
- Improved technology may drive down your costs in various areas of your business.
Diseconomies of Scale Definition
All of these economies of calibration tin occur as your company grows, and increases its product. But what happens if it grows also much?
Very large companies sometimes suffer from decreased efficiency. They may accept once had efficient labor specialization, but now in that location are simply too many people doing the aforementioned thing.
As well many layers of management, too petty control, as well many locations, and too many products are all potential sources of "diseconomies" of scale.
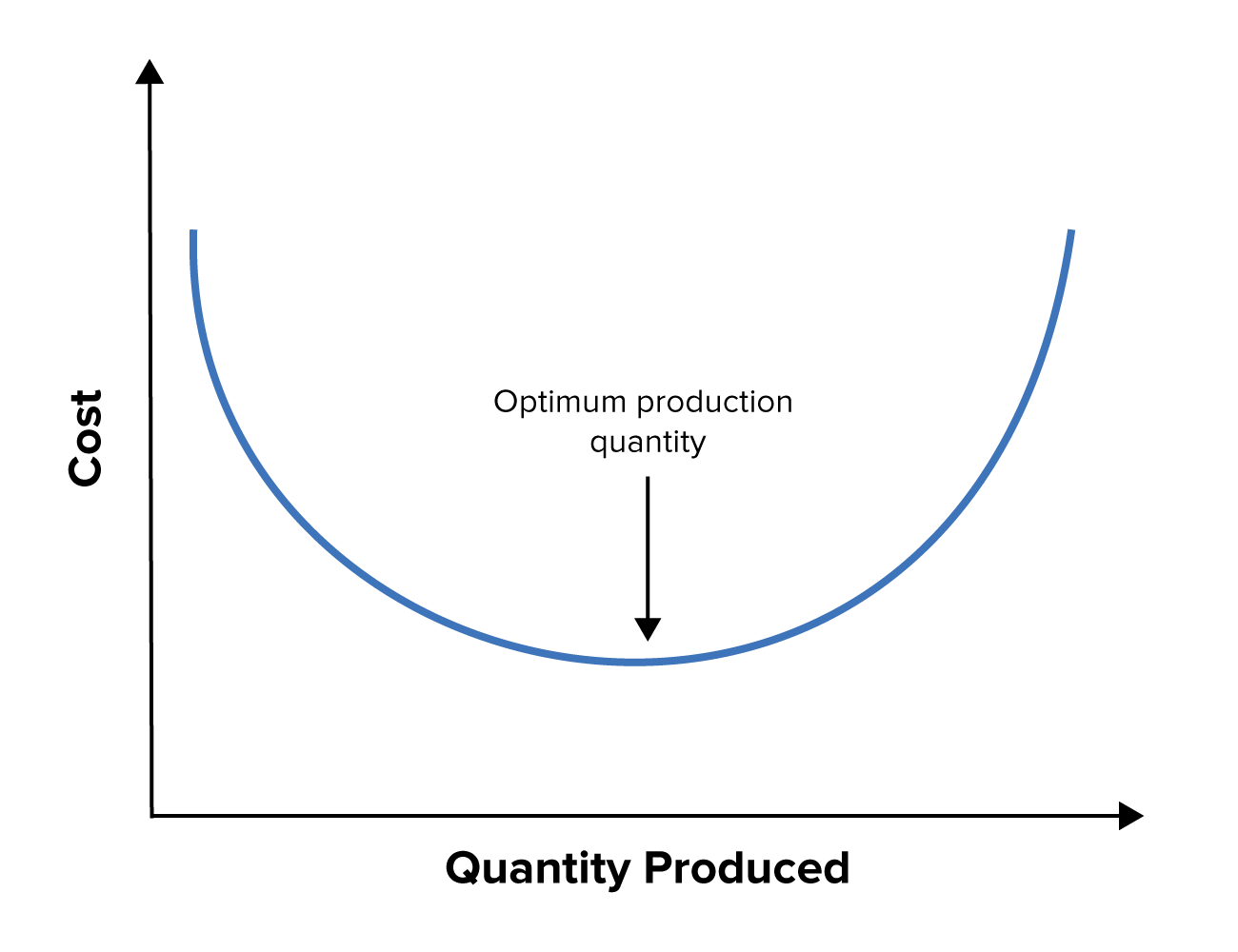
When this happens, average costs stop falling as product increases, and costs can starting time to rise once more as a result of this inefficiency. This signal is known as a company'southward "Minimum Efficient Scale." No further economies of calibration can exist achieved across this point.
This is illustrated in the U-shaped curve shown in figure 2, below.
The bottom of the curve is the optimal identify to be. At production volumes higher than this, the visitor's size is no longer an advantage.
Figure 2. Diseconomies of Scale by Cost and Quantity Produced

Cardinal Points
Economies of scale refer to the toll savings that organizations can make from efficient production processes that enable them to produce more for less. Taking reward of economies of calibration can have a number of benefits - information technology can enable companies to become more than cost competitive, make production processes more efficient, and improve profits.
At that place are two principal types of economies of scale:
- Internal – costs savings that are specific to a business or organization regardless of the industry it operates in. These can include technical, purchasing, managerial, financial, and risk-bearing economies of scale.
- External – this is when a company gains an advantage because of events and developments in its industry or the wider external environment.
Organizations must be careful near outgrowing their economies of scale and getting also big, equally this can cause diseconomies of scale. This is known as the "Minimum Efficient Calibration" and marks the betoken at which prices commencement to ascension again equally production increases because of inefficiencies.
Source: https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newSTR_63.htm

0 Response to "Marketing Channels Can Achieve Economies of Scale Through"
Post a Comment